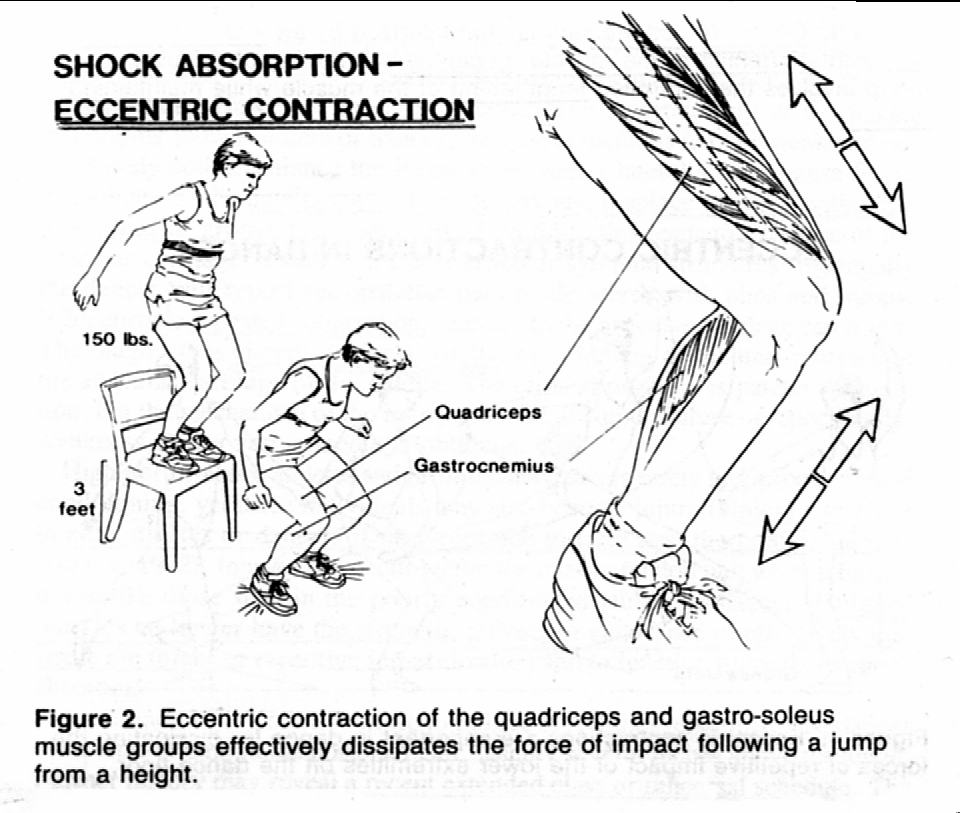
How the body absorbs force can be complex, but for Preliminary PDHPE you only need to know the basics and apply it to movement. Our body absorbs force by transferring the force to our muscles, where contractions in the opposite direction absorb the force. Some force is also absorbed by our bones and body tissue, but within sport most of our force absorption occurs in our muscles. In order to absorb large forces safely, our body seeks to absorb the force by increasing the time of absorption, increasing the movement length used to absorb the force, or increasing the area in which the force is absorbed. The body will also apply a force in the opposite direction, usually using an eccentric contraction.
The image to the right shows how this is achieved in the landing motion after jumping off a chair. The athlete bends at the knees, hips and ankles, whilst creating an eccentric contraction of the major muscle groups (quads, hamstrings, gluts, and calves) against the downward force. This contraction absorbs the force by creating an equal and opposite force cancelling out the applied force.
In order to increase the safety of the landing, the athlete can make the eccentric contraction go for longer by allowing a larger bend at the joints. Alternatively, the muscles can create a more forceful contraction to absorb more force over s shorter period, though this is harder to control.
Another example can be seen here on the left when catching a ball. The force from the ball is absorbed by the body through eccentric contractions in the shoulders, trunk and arms. These contractions absorb the force over a longer period of time, making it easier to control and increasing the chances of the athlete holding onto the ball.
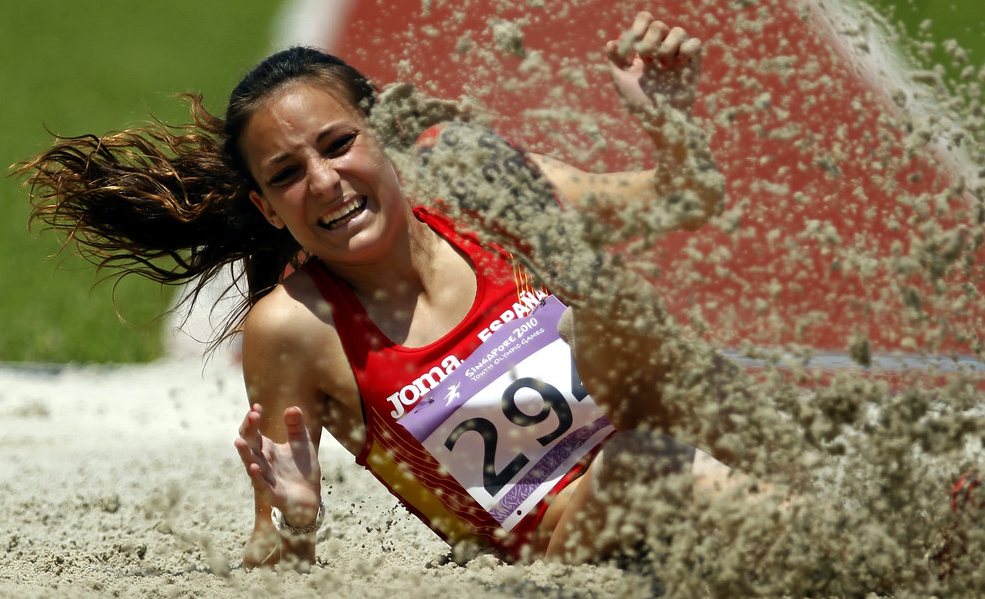
How does the body absorb force relates to movement and performance, because the longer the reaction force, or eccentric muscle contraction, the more control the athlete has over the movement. Performances such as catching in the field for cricket or baseball are improved by greater control over the balls movement and extending the period over which the force is absorbed. It is similar for gymnastics, where athlete’s often have to “stick” the landing. Here the better they are equiped to absorb the force over a set period of time, the better their landing will be as it will be controlled. Often ins sport equipment is used to help absorb forces, such as the gloves of a wicket keeper, or catcher, the mats used in gymnastics, or the sand in long jump. All help to absorb the forces in the sport.

