The muscular system is the second dot point under “How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?”. Muscles are the only organs in the body with the ability to contract and, therefore, their main function is to provide or cause movement. The muscular system includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle within the body.
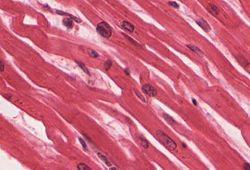
Cardiac muscle is the muscle that makes up the majority of the heart and allows the heart to contract (beat) and pumps blood around the body. It is a non-voluntary muscle and when viewed under a microscope has a striated appearance.
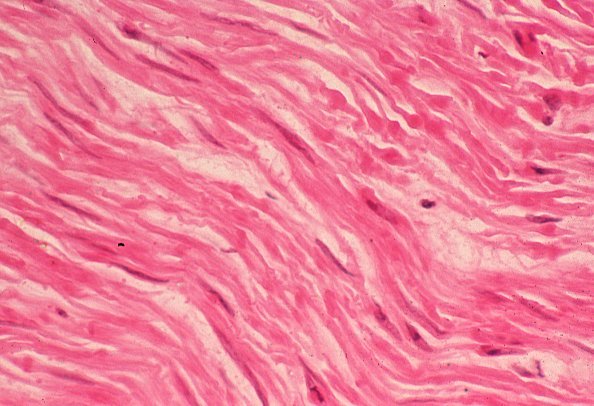
Smooth muscle is a non-voluntary muscle and often form cylindrical shapes around the outside of internal organs. Examples of organs with smooth muscle include the digestive and circulatory systems where the smooth muscle helps to control the diameter of the intestines, stomach, colon, and blood vessels.
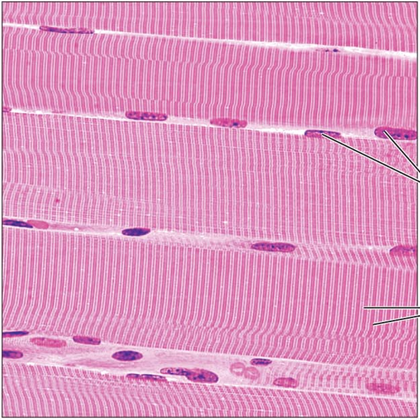
Skeletal muscle is the only voluntary muscle and has a striated appearance under the microscope. Skeletal muscles are responsible for providing the movements we perform every day and usually connect to bone via a tendon across skeletal joints.
The main focus in Preliminary PDHPE is on skeletal muscle, although you will also learn about cardiac muscle when you look at the circulatory system.
The Preliminary PDHPE syllabus says you need to:
Learn about:
- Muscular system
- Major muscles involved in a movement
- Muscle relationship (agonist, antagonist)
- Types of muscle contraction (concentric, eccentric, isometric)
Learn to:
- Identify the location of the major muscles involved in movement and related joint actions
- Perform and analyse movements, eg overarm throw, by examining:
- bones involved and the joint action
- Muscles involved and the type of contraction
Practice Questions
What are the major muscles that move the shoulder joint? 3 marks
Describe the different joint actions produced by various types of contractions in the biceps brachii? 4 marks
Describe kicking a ball in terms of the muscles related to the movement in the leg and the types of contractions. 6 marks
